Capstone Projects
Description:
The design and materials used in product packaging constitute a task of vital importance, and their development requires a methodical and rigorous approach to ensure the product’s success. The objective of the study was to understand how the purchase intention of a product like Yogurt varies based on packaging design and materials. The study was conducted among the Higher Education Institutions in Cuenca and was carried out in three key stages. In the first stage, the most relevant product for the study was identified, and the importance of packaging was justified, as it goes beyond its protective function, as a good package can influence the purchase decision. In the second stage, the Kano methodology was used to identify customer needs for the selected product, which was considered relevant in the first stage. In the last stage, the Kano methodology was applied to the results of the 404 surveys conducted. Fragments of Quality Function Deployment (QFD) were implemented, and based on the priorities of the obtained technical specifications, three basic design concepts were visually depicted using Cinema 4D software. A proof of concept was conducted, and design 3 received the highest score. This finding was contrasted with the results of a direct question that inquired about which design captures more consumer attention, and design 3 also came out as the winner. It is intended that this will be developed a posteriori and as future research it is proposed that the winning criteria can be taken and a new design can be made.
.
Description:
In all industries, it is important to apply effective process management focused on the fulfillment of goals and the satisfaction of needs exposed by the market. However, understanding its scope and limitations can be complex. The study aims to establish a standard, adaptable, and expressive tool for diagramming, improving its capacity in various industries. It focuses on the interaction with the main variables of a process: activities, managers and structure. Additionally, the study aims to impose a comparative analysis that answers the question of whether the BPMN is the best diagramming alternative compared to traditional graphic notations. The more important evaluation criteria are similarities, differences, the symbol library, diagramming software and types of processes as they are distinctive elements. Thus, the graphic notation selected as the best option will empower the organization towards maximizing benefits.
Description:
The following work addresses the issue of work-related stress in a company that manufactures textile products in the city of Cuenca. The objective is to carry out an analysis of the most relevant factors that generate stress both at a general level in the company as well as in its 4 work areas. The methodology used is based on 3 stages: data collection, statistical analysis and creation of a new model. To carry out this methodology, a standardized questionnaire based on the Control-Demand-Support model was used, and then using statistical techniques applied with SPSS software such as correlations, Chi-Square test and factor analysis, a deep and solid research was developed to clearly establish the state of the company in terms of stress. The results obtained were that the first hypothesis was not fulfilled, i.e. the level of stress found was moderate and not high. The second hypothesis was fulfilled, since the perception of stress is different, identifying that in work areas 1, 2 and 4 there is a moderate level of stress while in area 3 the level of stress found was low
Description:
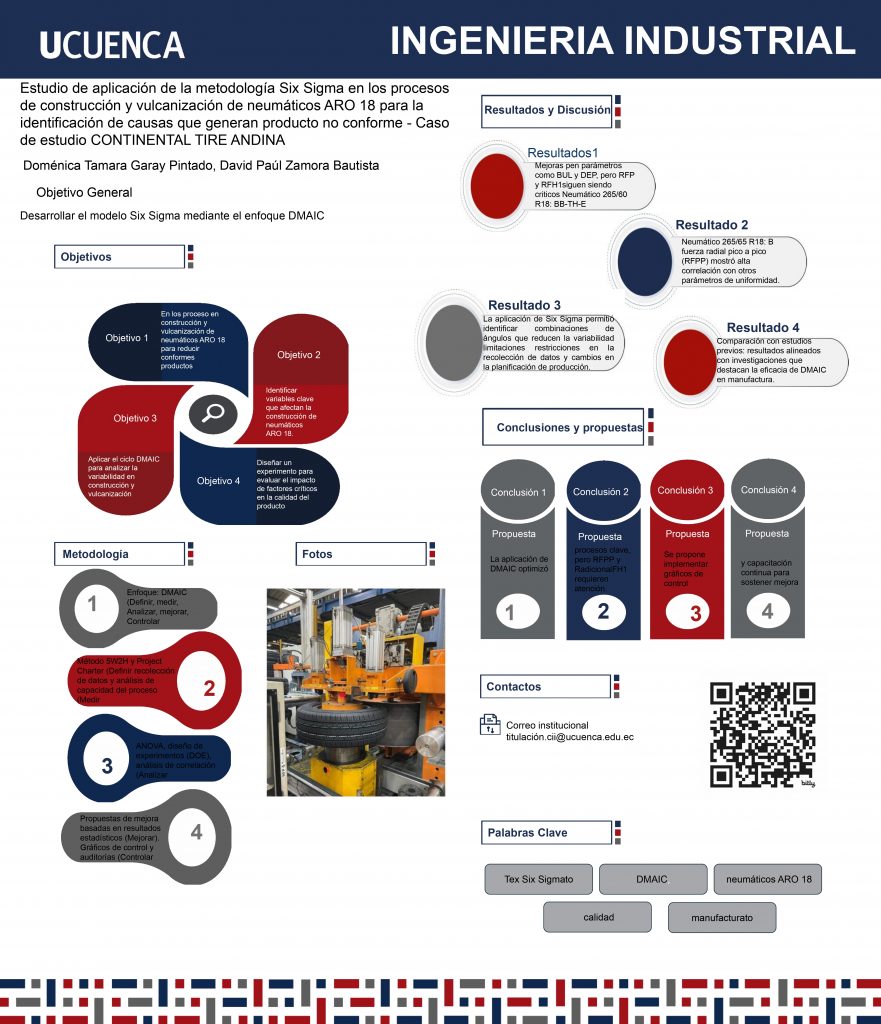
In the current business landscape, processes play a crucial role due to their impact on the efficiency, quality, competitiveness, and innovation capacity of organizations. Controlling these processes is essential to ensure product or service consistency, optimize resource use, reduce costs, and guarantee customer satisfaction through reliable and high-quality deliveries. This investigation demonstrates the use of the Six Sigma methodology in the construction and vulcanization processes by controlling critical quality parameters in two ARO 18 tires to minimize non-conforming materials. The variability of quality parameters was analyzed before and after the project’s implementation, focusing on three key manufacturing stages: two in construction (carcass, expansion) and one in vulcanization (curing). The Six Sigma methodology, through the DMAIC stages (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control), initially identified the causes of the uniformity problem using 5W 2H and conducted surveys with machine operators to pinpoint the most relevant factors for improving uniformity. A design of experiments and both descriptive and ANOVA statistical analyses were fundamental in controlling the processes and obtaining quantitative data on the effectiveness of changes in RIM 18 tire production. Based on the results, the optimal combination of components in each stage resulted in uniformity values within the company’s established limits, along with proposing improvement methods to maintain quality in future manufacturing processes
Description:
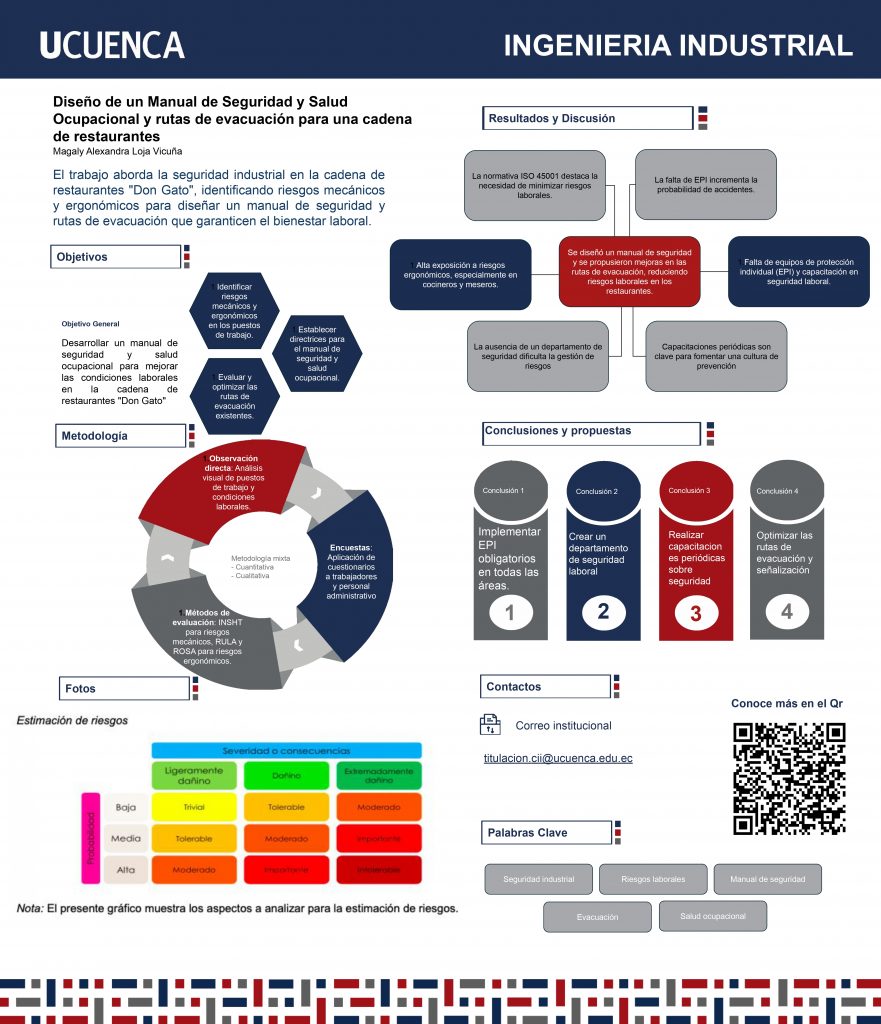
Industrial Safety is an issue that is addressed very insistently in organizations or companies dedicated to the production of goods or services that involve risks to the health and well-being of the worker; However, not all services with these characteristics are considered, for example, there is food service such as restaurants. In this degree work, Occupational Safety in the wholesale and retail trade, restaurants and hotels sector will be analyzed; In this case, the area of interest is the restaurants and the study was carried out at the suggestion of the owner of the “Don Gato” Restaurant Chain, Héctor Cabrera. The objective of this is to establish the level of occurrence of mechanical risks and ergonomic risks present, to subsequently design an Occupational Health and Safety Manual; The methodology to be used is a review of each of the jobs, analyzing their conditions and applying evaluations to each of the workers to corroborate the information obtained through visual analysis. In addition to this, the existing evacuation routes of each of the restaurants will be evaluated, in order to know their degree of effectiveness. Therefore, upon completion of this degree work, the restaurant chain of interest will have all the security measures established to guarantee the work well-being of its workers, customers and managers.
Description:
The banana sector is the main economic activity of the province, especially in the city of Machala, being recognized for its agricultural production, especially in banana production. Although banana exports follow strict quality standards, a considerable volume of rejected fruit is generated. Despite not meeting export criteria, this fruit is still suitable for human consumption. This presents an opportunity to take advantage of rejects as raw material in the production of banana flour, which would generate additional income for producers. The objective of this research work is to evaluate the technical and economic feasibility of implementing a system to produce banana flour from the rejects of a producer and exporter in the city of Machala. To do this, the current situation of the company, the production processes and the volume of fruit considered as rejects were first analyzed. A market study was then carried out to determine the potential demand for the product. Then, a technical analysis of the infrastructure necessary for processing and an economic analysis was carried out that includes the initial costs and the expected income from the sale of banana flour. The results obtained demonstrate that the farms generate a significant amount of rejects suitable for the project and that the existing infrastructure can be adapted for flour production, demonstrating that the project is financially profitable over time. In conclusion, this study provides compelling evidence that establishing a banana flour production system from rejects is a viable and beneficial measure, not only from a technical and economic point of view, but also from an environmental sustainability and reduction of agricultural waste.
Description:
This degree work addresses the challenges of the Ecuadorian textile sector, proposing a production model based on Industry 5.0 for a company in the city of Cuenca. The main objective is to integrate sustainability and resilience factors to improve the competitiveness of the sector. The methodology used is developed in three phases: Diagnostic phase: review of industry 5.0 literature, selection of indicators, preparation, and application of surveys; Production Model: evaluation of results, analysis of critical indicators and proposal of a production model based on the diagnosis and concepts of industry 5.0; Improvement Cycle: preparation of an improvement proposal and evaluation through simulation. It was revealed that, of the 82 indicators evaluated, 62 showed positive performance. On the other hand, 20 of the evaluated indicators require immediate attention, 11 classified as “inadequate” and 9 as “unacceptable”. The proposed model integrates productive efficiency, sustainability, the human approach, and resilience, focusing especially on planning, manufacturing, and packaging. The model considered the axes of sustainability, the result of the initial diagnosis, so improvement strategies were proposed for the critical indicators obtained. Among these, the implementation of automation stands out to reduce the workload and, simultaneously, improve the well-being of employees. This multifaceted approach not only seeks to optimize the processes of the company studied, but also to provide a versatile model applicable to other companies in the sector, thus contributing to the sustainable growth and positive transformation of the Ecuadorian textile sector
Description:
Effective inventory management is essential to optimize the control, storage and distribution of products within a system. In this study, an approach based on statistical analysis and machine learning algorithms was used to determine the optimal classification of items in an automotive parts inventory system. For this purpose, a database containing the spare parts sales of an automotive company over the course of a year was examined. By applying the Kmeans, Clustering Large Applications (CLARA) and Divisive Analysis (DIANA) algorithms, an optimal classification distributed in three clusters was identified. In addition, a comparative analysis with the ABC classification was performed to define the characteristics of each cluster. The results showed that the CLARA algorithm improves inventory management, allowing to optimize storage space, increase operational efficiency, reduce costs, improve customer service and make informed decisions. It can be mentioned that, some outstanding products in the resulting clusters were 2452084002, 5810159A00 and 3910045800 from clusters 1, 2 and 3 respectively; these products are relevant due to their total sales in each cluster relating their quantity, cost and sales price. This study contributes to the field of inventory management by demonstrating how the use of machine learning algorithms through statistical analysis can optimize the classification of items in the inventory, being relevant in strategic decision making through a more accurate distribution adapted to the needs of the company.
Description:
The objective of this research was to develop a quantitative instrument to measure the objective factors that impact the competitiveness of associative ventures. The study was carried out in three main stages. First, a literature review was carried out to find and understand the factors that affect the competitiveness of these ventures and relate them to the concept of value chain. This review provided a solid theoretical foundation for the development of the tool. In the second stage, specific indicators were defined for the identified factors, qualification metrics were established and a tool was built to quantify the performance of the value chain in associative ventures, using Porter’s value chain model (1980) as a reference and the quantification methodology of Arce and Calvez (2008). This detailed process ensured the relevance and applicability of the indicators and metrics. Finally, in the third stage, the tool was validated through its application in three case studies selected by convenience sampling, covering different levels of competitiveness and sustainability of associations of the popular and solidarity economy in zone 6. This practical validation made it possible to evaluate the effectiveness and precision of the tool in real contexts, providing valuable information about its applicability and usefulness in improving the competitiveness of associative ventures. The result was a robust tool that facilitates the measurement and analysis of the key factors that influence competitiveness, offering associative ventures a practical solution to evaluate the value chain of associations.
Description:
This research work focuses on proposing a competitiveness model based on BlockChain technology in a supply chain oriented to secure IT processes (traceability, transparency and immutability), focusing on the production of medicinal plants in the parish of Susudel. The farmers of the “Luz y Sal” foundation, who are mostly elderly farmers, grow plants in greenhouses using conventional techniques, which is why this research proposes to implement BlockChain technology. The study evaluates specific indicators obtained from a literature review, as well as indicators proposed by the authors as shown in Table 3 and Table 4, in order to measure the behavior of the chain before and after the implementation of blockchain. For this purpose, Vensim PLE software and System Dynamics were used as tools for the creation of the competitiveness model. The model was validated using the case study of the “Luz y Sal” foundation, where it was demonstrated that the implementation of BlockChain significantly improved transparency and traceability in the supply chain. This technology optimized the transfer of information along the chain, which facilitated flexibility to respond to fluctuating demands. In addition, the immutability of records and the ability to trace products generated greater trust among stakeholders.